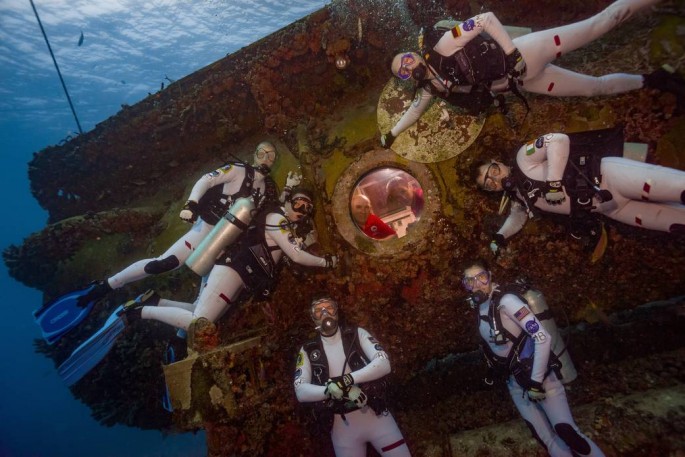
NASA sent some astronauts under the depths of the Atlantic Ocean to carry out a 16 day mission, that will help them for the preparation for deep space missions, more specifically the first manned mission to Mars by the 2030s.
The team of astronauts will receive some deep sea training as a space mission simulation where the bottom of this massive ocean is apparently similar to the dry, Red Planet as they are both extreme environments.
This mission is known as NEEMO 21 (NASA Extreme Environment Mission Operations) expedition that already began in July 21. This international crew will be able to test out some new tools and methods for future space explorations and more importantly, to live within spacecraft conditions with this underwater environment. In addition, simulated spacewalks will be carried out from their underwater habitat known as the Aquarius.
For this deep sea mission some 62 feet below the ocean, the Aquarius Reef Base is located off the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. The crew will be subjected to isolation that can mimic life and work in microgravity environments such as the International Space Station and eventually, spacecraft that will embark on long spaceflights towards asteroids and planets.
According to NEEMO project lead, Bill Todd, the NEEMO 21 astronauts and crew will be the pioneers in completing complex tasks from the seafloor with the most advanced underwater navigation and scientific tools that are all choreographed to simulate a Martian traverse during exploration.
Inside the habitat, the crew should be able to carry out a variety of research and operations studies like testing out a mini DNA sequencer similar to the one that is testing aboard the space station right now, including a telemedicine device that can be utilized for space applications in the future.
For the simulated spacewalks, the crew should also be able to collect marine biology samples and geological studies, along with testing software and managing operations, which ultimately completes a coral restoration project. This will also include communication delay tests that can also be encountered during Martian missions.