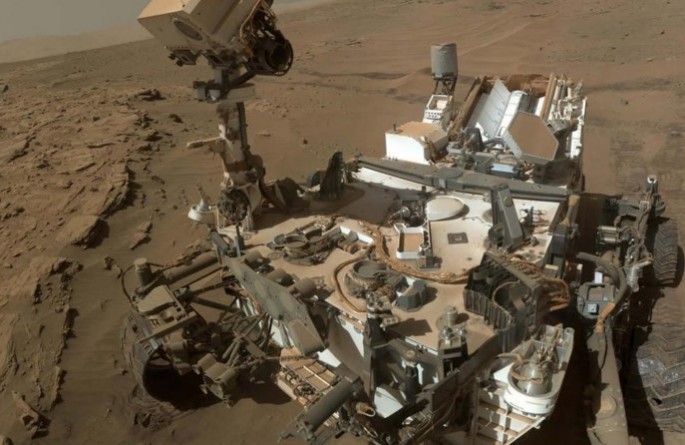
Methane is believed to be an indicator of life in Mars. While a new study revealed another source of methane surge on the Red Planet, the gas is viewed to post health risks to Earth ecosystems.
California Institute of Technology and NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) lead author Rnyu Wu told Space that methane usually became stuck onto Martian soil particles in dry conditions. Wu added that when salts called percholates deliquensced or became liuid after absorbing atmospheric water, the gas was then released into the air.
Wu also mentioned that National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)'s Curiosity encounterned a random and localized methan upsurge that had previosuly been contained in a subsurface aquifier, which is another theory about methane's non-life idea.
According to Wu, life, perchlorate deliquescence, and random surge, are three possibilities that could be tested to some degree, utilizing future Curiosity observations.
Wu explained that life and perchlorate deliquescence are predicted to yield methane flare-up in nearly the same timeline in each Martian year, as they are both associated to the deliquescence cycle. Liquid water could activate dormant organism, in case of life. On the other hand, random methane outburst is not expected to have a seasonal timing.
In 2014, Curiosity's 1-ton rover found an upsurge in methane levels at its landing site, Gale Crater. After measuring the gas levels four times in two months on Mars, the average gas levels rose ten fold before it quickly spread out and disappeared.
While the presence of methane on the Red Planet ignited scientists interest on investigating the potential of life on Mars, the gas is viewed as a climate threat on Earth.
The rise in surface temperature heat lakes across the planet, creating blooms of algae that are toxic to fish and take oxygen levels from water, according to Express UK. Aside from its toxicity to the lake inhabitants, the algal blooms also yield the methane, which is 25 times more capable than carbon dioxide at global warming.
Accodring to NASA, the rise in water temperature affects several propertiees that are vital to the health and viability of the ecosystems. With this warmer water temperature measurements caused by increased methane production, life forms are assumed to change and even vanish.