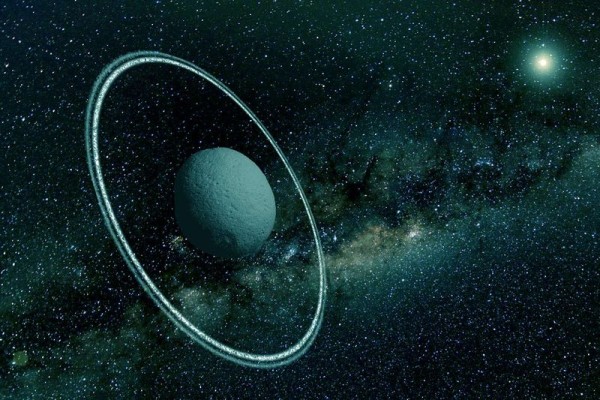
Researchers have recently detected jets, dusts, and rings around Chiron.
Throughout history, the solar system is known to having five bodies that bear rings. The most popular is Saturn; however, rings of dusts and gases also surround Neptune, Uranus, and Jupiter. Chariklo is the list's fifth member, belonging to centaurs, a class of minor planets that have characteristic rocky, small bodies.
Chariklo's ring system has only been detected recently and came as a surprise because centaurs have been dormant for years. Scientists at MIT have seen a possible ring system surrounding Chiron, a second centaur.
Chiron was discovered in 1977 and considered the first planet to be categorized under the "centaur" group. The name was derived after a mythological creature that is half beast, half man.
The group from MIT was able to detect the stellar occultation in November 2011, where Chiron passed by a bright star, blocking its light briefly. The researchers analyzed the light emissions, momentary shadowing, and all other optical features that could suggest Chiron's possibility of possessing a circulating disk. The team strongly believes that all these signify a ring system composed of dust and gas, or of symmetric jets shooting in an outside direction.
"It's interesting, because Chiron is a centaur - part of that middle section of the solar system, between Jupiter and Pluto, where we originally weren't thinking things would be active, but it's turning out things are quite active," Amanda Bosh of MIT's Department of Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences said.
Bosh, alongside MIT colleagues Amanda Gulbis, Michael Person, and Jessica Ruprecht, published these findings in the Icarus Journal.