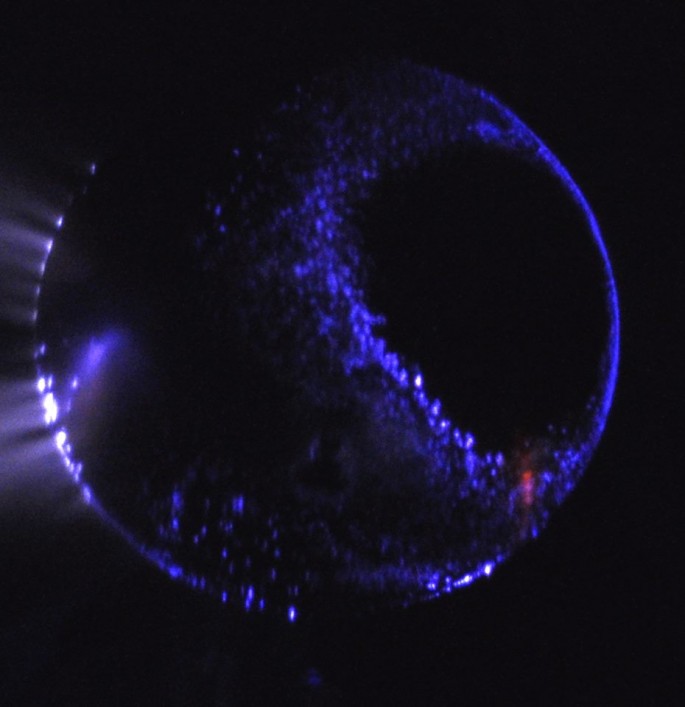
Colorful auroras occasionally light up Mars' skies, an event noted years ago but was only confirmed recently by an international team of astronomers. More than that, the stunning spectacle may be observed by the naked eye.
The first unconfirmed observation was in 2005 by the SPICAM imaging equipment, which caught images from space while on board the European Space Agency (ESA) satellite Mars Express.
In March, NASA's MAVEN mission, which orbited Mars 1,000 times, confirmed the 2005 observation, adding that it could be seen by humans on the red planet's surface, NASA reported on May 28.
Astronomers have previously known the existence of auroras in other planets and moons in the solar system like Jupiter's Ganymede. However, it was only recently when they confirmed that the light display could be seen by the naked eye on Mars' surface when humans start habitating the planet.
This means the Earth is not the only terrestrial planet where an aurora could be seen by the naked eye.
Auroras are a result of a complex interplay between the planet's magnetosphere and charged solar particles entering the atmosphere. When the atmosphere's molecules heat up, the solar particles deactivate and radiate light in various colors. In Mars' case, it is deep blue.
In December last year, astronomers were stunned by a unique aurora display they refer to as Mars' "Christmas Lights" which glowed erratically and strongly, Nature World News said.
The recent observation has brought the team new insights to the red planet's atmospheric characteristics, its evolution and differences or similarities to Earth's.
Ultimately, however, they hope the research can help them find habitable planets.