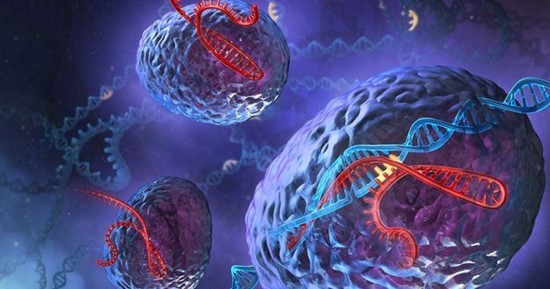
Scientists have reached another milestone - an enhanced gene editing tool called CRISPR-Cas9.
CRISPR-Cas9 enables scientists to generate minute changes on the details of particular genes in the cells, according to NPR. It is not the first time scholars managed to develop such innovation, since techniques like zinc finger nucleases and Talens were already made in the past. However, they were difficult to use that they were not adopted at a wide interval.
CRISPR is viewed as the "breakthrough of the year," as per the journal "Science." It was revealed that the innovation had already appeared twice before, in 2012 and in 2013, where it stood as a runner-up, along with other genome-editing techniques.
This year, CRISPR unleashed its inner potential, allowing it to overrun other advancements in the field of genetics. Cases in point included the purposive modification of the human embryo DNA and the completion of the much anticipated "gene drive," which could completely remove pests and the diseases they carry.
CRISPR's simplicity and accessibility are the two major traits of the innovation that sets it apart from other companies that utilize designer proteins. Such primary traits, along with its dependability, allowed CRISPR to transform society, said by Stanford University bioethicist Hank Greely in a statement.
Some major discoveries with the rise of CRISPR include the awareness that bacteria could also remember viruses, which resembles the immunological memory of the body's immune system. In addition, the CRISPR-powered gene drive followed and it involveed gene attachment for a desired trait to "selfish" DNA elements that could duplicate themselves from one chromosome to another.
For the time being, genome-editing techniques are the focus of the public in high-profile gatherings and magazine articles, placing CRISPR as an early lead among modern innovations. It is followed by Pluto, which was circled by the New Horrizons probe in July.
CRISPR can nearly do anything; however, one ethical concern it faces is whether it should be allowed or not.